Building Technologies to Improve Environmental and Sustainable Impact
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Construction |
| ✅ Wordcount: 1489 words | ✅ Published: 03 Nov 2020 |
Abstract
The main purpose of this report is to suggest two building technologies which can be implemented to improve the existing details which may have an environmental and sustainable impact. With this said, limitations which need to be taken into account such as current state in which the building is in, where the building is situated and the use of the building. An energy performance table along with drawings and figures will be presented to demonstrate the efficiency of the systems. Research for this rationale included energy-efficient systems that are specific to reducing energy consumption while the building is in use, passive design and energy-efficient systems. Studies carried out by experts estimate how heat is lost in buildings, the results are: up to 30% in loss due to poor resistance to heat transfers in building envelope, up to 40% due to unorganised and organised infiltration of heated air and up to 30% due to unregulated heating systems and unnecessary use of hot water. With this said it can be assumed that an innovative approach towards the design of structural systems, development of equipment and products and improved building materials will be taken satisfying the requirements of feasibility, cost effective, environmentally safe, energy conservation, easily adaptable and low complexity of construction.
Introduction
Compared to old building regulations, the heat transfer resistance required has increased according to current building regulations. Due to rising cost of thermal energy it is critical to increase the thermal protection in buildings in order to reduce these costs while the building is in use. The use of insulation during construction of the external walls, partitions and ceilings is a way to increase the energy efficiency of a building. However, there are limitations.
Limitation one – the current design of the building. Due to the use of single glazed curtain wall around the perimeter of the building as seen in figure 2 , the building has an issue with thermal loss. Although the curtain wall is said to be aesthetic pleasing, a disadvantage of this is that it causes condensation and as seen in figure 1, this is the reason as to why heaters are placed directly in front to stop the windows steaming up.

Figure 1 – Heater placed directly in front of curtain wall
Limitation Two – Location of the building. It is important to take into consideration the wider role in which this area contributes to in terms of London’s world class capital city status, policy S28- Design, was put in place and indicates what the development should include in terms of architecture, sustainability and design the reduction of emissions and energy use is also discussed. Westminster City Plan 2016 states ‘development in Westminster is often about refurbishment and renewal of building stock rather than significant land use change’.
Limitation Three – the use of the building. The building in question is a live university and there are a limited number of weeks that a contractor refurbishing the building can have to do so as the remaining weeks are during term time for students and staff attending the university. This rationale will discuss all the above mentioned and make suggestions to overcome these.

Figure 3 – Close up of singe glazing around the perimeter of the building
Curtain Wall
Generally, most translucent façade design is a structural frame that a wide range of shapes, functions and materials can be included. Although there are many types and forms of external translucent curtain walls, they are mostly have the same fundamental structural principles, as seen in figure 3.

Figure 3 – Curtain Wall Detailed Drawing
Panels are separated into opaque and translucent. Opaque panels are often made of stone, metal, glass and translucent panels are often made with glass. Behind the panels there is usually thermal insulation, an air cavity and an airtight duct. A glass filling is often installed within the façade frame with a silicone sealant or rubber seals, in some cases a point fastener is used. When looking at the project building as seen in figure 4 and figure 5, the façade looks like a muillion-transon system where individual parts are mounted and installed on site using a crane. Racks are placed vertically onto the supporting structure, the crossbars are installed horizontally between them, then finally the filling panels are installed with a shading material.


Figure 5 – Front façade of building
Figure 4 – Front façade of building
Post-bar facadee systems are standard items that are always availablefor procurement. This inturn means they are a relatively cheaper than one-off systems with a unique design. Also the cost to delievr this syte to site is relatively low as the components are easily compatiable and can be installed. However, there are disadvantages that this system encounters from how it is assembled on site. These include the accuracy of the human eye when compared to being assembled in a factory with a machine, potential quality issues, higher cost of labour and the pace of work will be slower. With this said this system along with the crossbar system are usually only used for buildings which are no larger than medium height.
To solve the current thermal loss issue that the current curtain wall is causing it can be refurbished using a customised energy effiencient glass (low-e) as seen in figure 6. This product has double low emission transparent warm glass inside the building with tinted heat which is reinforced on the outside of the building. The main functions of this product is that it is sound insulating , reduced solar heat and gain, provides users with a comfortable cooler indoor in the summer and warmer indoors in the winter.
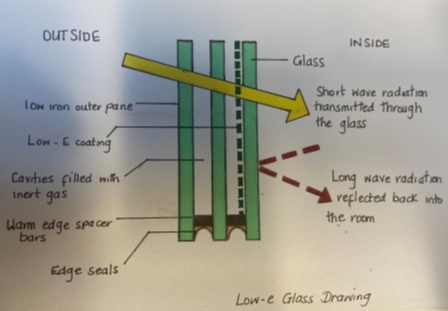
Figure 6 – Low-e Glass Drawing
Ventilated Façade
There are two most common type of installation of external walls, these are non-ventilated and ventilated facades. Non-ventilated facades use polystyrene plates and wool which fasten on to the frame or the wall directly and ventilated facades which allows for the formation of an air chamber between the exterior wall and the cladding. It is important to mention the following technical information when discussing functionality. Multi-layer concrete wall and floor systems are the most energy-efficient systems for exteriors walls.
Ventilated facades systems provide sound insulation was well as effective thermal protection. This system can be designed in many different solutions as suppliers are able to offer a wide variety of cladding panels in different colours and designs. Costs to service and maintain such systems and minimal and can be repaired easily when required. Figure 2 is the most common type of façade used, with the help of a bearing bracket which is attached to the supporting wall, which the profile is fixed to as seen in Figure 7. Some advantages of ventilated systems include installation can be carried out in any weather condition, aesthetically pleasing, excellent sound protection, covers any defect in the wall and due to the low complexity of design this increases the efficiency of maintenance and repair.
From experience, the effect of energy conservation can be met by the modernization of the existing facilities by introducing new energy sources, equipment and systems. Some suggestions of how this can be achieved are ensuring that there are specific modes set for heating during the times when the building is in use, mode set for when the building is closed, different modes for during the different seasons i.e. winter, spring, autumn and summer. Also, the use of a high performance boiler when if placed on the roof of the building saves the need to use of heating networks.

Figure 7 –Example of Ventilated Façade
Conclusion
Summing up, it can be assumed that within the next few years, the sue of energy efficient and energy saving materials in traditional construction projects will be on ensuring the design and construction of buildings have minimal heat loss throughout with the use of materials and products have a high coefficient resistance to heat transfer. With this said, going forward design and manufacture of products, equipment, structural systems and materials will satisfy the requirements of feasibility, cost effectiveness, environmentally safe, energy conservation, easily adaptable and low complexity of construction in both commercial, higher education and residential building.
References
- Bricker-project.com (2019). Passive technologies can maximise primary energy reduction and economic investment in existing buildings. [online] Available at: http://www.bricker-project.com/news/interviews/matteo-dantoni–in depth-analysis-required-prior-to-retofitting-old-buildings.kl [Accessed 7 Dec.2019].
- Bricker-project.com (2019). Revamping existing buildings to make them energy efficient. [online] Available at: http:// www.bricker -project.com/news/interviews/a.kl [Accessed 2 Jan. 2020].
- Cse.org.uk (2019) Energy efficient glazing | Centre for Sustainable energy. [online] Available at: https://www.cse.org.uk /advice/advice-and-support/energy-efficient-glazing-double-glazing [Accessed 13 Dec. 2019].
- Level.org.nz (2019). Options for wall insulation. [Online] Available at: http:// www.level.org.nz/passive-design/insulation/options-for -wall-insulation [Accessed 14 Dec. 2019]
- Li, X., Shen, C. and Yu, C. (2017). Building energy efficiency: Passive technology or active technology?. Indoor and Built Environment, 26(6), pp.729-732.
- Peach, C. (2016). Structural Membranes used in Modern Building Facades. Procedia Engineering, 155, pp. 61-70
- Vatin, N. (2015). Innovative Technologies in development of construction industry. Zurich: Trans Tech Publishers.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal



